10th Workshop on Building and Using Comparable Corpora
SHARED TASK
Shared task: identifying parallel sentences in comparable corpora
We announce a new shared task for 2017. As is well known, a bottleneck in statistical machine translation is the scarceness of parallel resources for many language pairs and domains. Previous research has shown that this bottleneck can be reduced by utilizing parallel portions found within comparable corpora. These are useful for many purposes, including automatic terminology extraction and the training of statistical MT systems.
The aim of the shared task is to quantitatively evaluate competing methods for extracting parallel sentences from comparable monolingual corpora, so as to give an overview on the state of the art and to identify the best performing approaches.
| Shared task sample set released | 6 February, 2017 |
| Shared task training set released | 20 February, 2017 |
| (Chinese training set released) | 3 March 2017 |
| Shared task test set released | 21 April, 2017 |
| Shared task test submission deadline | 28 April, 2017 |
| Shared task paper submission deadline | 2 May, 2017 |
| Shared task camera ready papers | 26 May, 2017 |
Any submission to the shared task is expected to be followed by a short paper (4 pages plus references) describing the methods and resources used to perform the task. This will be accepted for publication in the workshop proceedings automatically, although the submission will go via Softconf with the standard peer-review process.
Shared task data contents
Sample, training and test data provide monolingual corpora split into sentences, with the following format (utf-8 text, with Unix end-of-lines; identifiers are made of a two-letter language code + 9 digits, separated by a dash ’-’):
- Monolingual EN corpus (where EN stands for English), one tab-separated sentence_id + sentence per line
- Monolingual FR corpus (where FR stands for Foreign, e.g. French), one tab-separated sentence_id + sentence per line
- Gold standard list of tab-separated EN-FR sentence_id pairs (held out for the test data)
Datasets are provided for French-English, German-English, Russian-English, and Chinese-English (see links below).
Important information and requirements:
- The paper that describes the data preparation process (BUCC 2016) transparently explains that the data come from two sources: Wikipedia (now 20161201 dumps from December 2016) and News Commentary (now version 11). The details of corpus preparation have changed since the paper, but its overall principles remain the same.
- As a consequence, the use of Wikipedia and of News Commentary (other than what is distributed in the present shared task corpora) is not allowed in this task, because they trivially contain the solutions (the latter in a positive way, and the former in a negative way).
Sample data
Sample data is provided for the following language pairs (note that the monolingual English data vary in each language pair):
Each sample dataset contains two monolingual corpora of about 10–70k sentences including 200–2,300 parallel sentences and is provided as a .tar.bz2 archive (1–4MB).
Training and test data
Training and test data are provided for the following language pairs (note that the monolingual English data vary in each language pair):
- de-en (German-English)
- fr-en (French-English)
- ru-en (Russian-English)
- zh-en (Chinese-English)
- download training data
- download test data
Each training or test dataset contains two monolingual corpora of about 100–550k sentences including 2,000–14,000 parallel sentences and is provided as a .tar.bz2 archive (6–36MB). Training data includes gold standard links, test data does not.
Task definition
Given two sentence-split monolingual corpora, participant systems are expected to identify pairs of sentences that are translations of each other.
Evaluation will be performed using balanced F-score. In the results of a system, a true positive T P is a pair of sentences that is present in the gold standard and a false positive FP is a pair of sentences that is not present in the gold standard. A false negative FN is a pair of sentences present in the gold standard but absent from system results. Precision P, recall R and F1-score F 1 are then computed as:
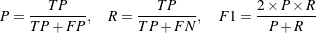
Submission details
Each team is allowed to submit up to three (3) runs for each language. In other words, a team can test several methods or parameter settings and submit the three they prefer.
Please structure your test results as follows:
- one file per language, named <team><N>.<fr>-en.test, where
- <team> stands for you team name (please use only ASCII letters, digits and “-” or “_”)
- <N> (1, 2 or 3) is the run number
- <fr> stands for the language (among de, fr, ru, zh)
- the file contents and format should be the same as the gold standard files provided with the sample and training data, and contain only those sentence pairs that the system believes are translation pairs:
- One sentence_id pair per line, tab-separated, of the form <fr>-<id1><tab><en>-<id2> where <fr> is one of de, fr, ru, zh and <fr>-<id1> and en-<id2> are 9-digit identifiers found in
the <fr> and en parts of the test corpus. For instance, for de-en (German-English):
de-000000003<tab>en-000007818
de-000000004<tab>en-000013032
...
- One sentence_id pair per line, tab-separated, of the form <fr>-<id1><tab><en>-<id2> where <fr> is one of de, fr, ru, zh and <fr>-<id1> and en-<id2> are 9-digit identifiers found in
the <fr> and en parts of the test corpus. For instance, for de-en (German-English):
- put all files in one directory called <team>
- create an archive with the contents of this directory (either <team>.tar.bz2, <team>.tar.gz, or <team>.zip)
Send the archive as an attachment in a message together with factual summary information on your team and method:
To: bucc2017st-submission@limsi.fr
Subject: <team> submission
Team name: <team>
Number of runs submitted: <1,2,3>
Participants:
<person1> <email> <affiliation> <country>
<person2> <email> <affiliation> <country>
...
Resources used: <dictionary X>, <corpus Y>, ...
Tools used: <POS tagger X>, <IR system Y>, <word alignment system Z>, <machine learning library T>, ...
You will receive a human acknowledgment in a maximum of 8 hours (depending on the difference between your time zone and CEST).

